Shedding of grafts after Hair Transplant
Shedding of grafts after the hair transplant is considered to be normal and one should not be worried about it. On average you might lose 50-100 hair a day. It is, however, important to clearly distinguish between normal shedding and the post-operative shedding of transplanted hair grafts.
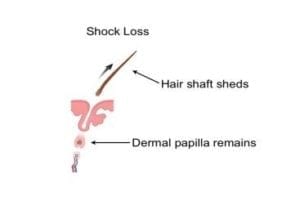
Shedding of Transplanted Hair
Shedding of transplanted hair is an almost universal characteristic of a hair transplant. This occurs because during hair transplantation a graft is temporarily stripped of its blood supply. As a response to this insult, the grafts shed their hair. Shedding of transplanted hair is noticed beginning one week following the procedure and continuing for up to six weeks. A very small percentage of patients do not shed and the transplanted hair continues to grow. In others, the transplanted hair remains on the scalp for months until a new hair pushes it out. It is important to note that whether a patient sheds or not has no bearing on the outcome of the hair restoration.
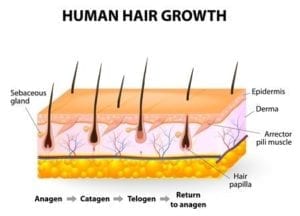
Shedding of Normal, Non-Transplanted Hair
Hair goes through a cycle of growth and shedding made up of the anagen, catagen, and telogen stages. This cycle, unlike the hair growth cycles of other mammals, is completely random, and a varying number of hairs can be in any one of these phases at any given time.
The anagen phase is otherwise known as the active phase of hair and lasts for about 2-6 years. During this phase, hair grows about 1cm every 28 days. The catagen phase is referred to as the “transitional phase”, and lasts for 2-3 weeks. At any given time, about 3% of all hairs are in this phase. The telogen phase, otherwise known as the “resting” phase, is where most shedding occurs. About 6-8% of all hairs can be in the telogen phase and can last for about 100 days. During this time, as much as 50-100 hairs are shed.
How to Reduce Hair Shedding After a Hair Transplant
Though hair graft shedding or shock loss is unavoidable, there are a few things you can consider in order to minimize the number of hairs lost after a hair transplant.
- Medication: Propecia (finasteride) halts or reverses miniaturization in many individuals and its use may decrease the risk of shedding following hair transplants. Its ability to prevent shedding, however, has not been proven in controlled studies.
- Timing and Size of Hair Transplant: Many patients choose to have a hair transplant at the onset of hair loss or when they have significant miniaturization. When patients take this kind of approach, their hair often ends up looking thinner than it did before the procedure was performed because the progression of the hair shedding was not taken into account.
- Camouflaging Products: Patients may opt for cosmetic camouflaging products that can disguise the physical evidence of hair shedding and hair thinning. These products cover up balding areas by adding volume and lift to the base of the hair shafts, incorporating hair building fibers for fuller coverage and thickness, and employing topical shading to disguise bare spots on the scalp.
Call us today and book your exclusive consultation session with our doctor!
All you want to know about PRP Therapy
All you want to know about PRP Therapy PRP, which...
Read MoreGenetic Hair Loss Medical Therapies for Men & Women
Genetic Hair Loss Medical Therapies for Men & Women We...
Read MoreBody Building & Hair Fall – Myth or Real?
Body Building & Hair Fall – Myth or Real? Bodybuilding...
Read More



